The Fascinating Mechanics of Hearing Explained
Understanding how hearing works is crucial for anyone entering the medical field, especially in regions like Uganda and East Africa, where access to healthcare professionals may be limited. This article delves into the anatomy of the human ear and the intricate processes involved in hearing, shedding light on how sound waves are transformed into signals our brain can interpret.
In How Hearing Works (3D Anatomical Model), the discussion dives into the mechanics of hearing, exploring key insights that sparked deeper analysis on our end.
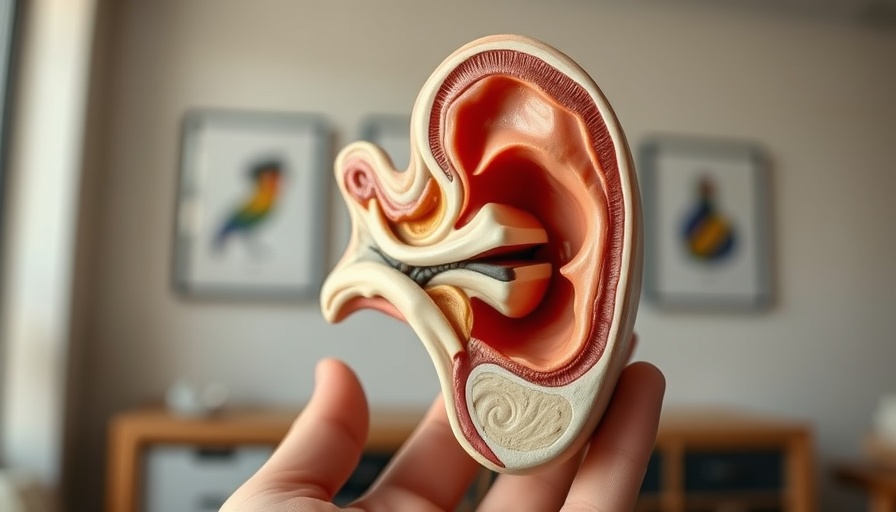
Unpacking the Anatomy of the Ear
The ear consists of three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Each section plays a unique role in the process of hearing. The outer ear gathers sound waves, which then travel through the ear canal to the eardrum. Once the sound waves hit the eardrum, they cause it to vibrate, which is where the middle ear comes into play, as the vibrations are transferred to the tiny bones called ossicles. These bones amplify the sound and pass it on to the inner ear.
The Importance of the Inner Ear: Translating Sound Into Signals
In the inner ear, the cochlea—a spiral-shaped organ—houses hair cells that convert vibrations into electrical impulses. These impulses travel via the auditory nerve to the brain, where sound is interpreted. Understanding this translation process is vital in diagnosing and treating hearing impairments that may affect the community.
Understanding Auditory Health: Why It Matters
Hearing is often taken for granted, yet it greatly affects daily life and communication. In Uganda, where many are still becoming familiar with audiology and its significance, embracing knowledge about hearing can lead to early detection of hearing issues and better public health responses. Medical students and healthcare workers must prioritize training in auditory health protocols to improve patient outcomes.
Future Trends in Audiology and Hearing Technology
With advancements in technology, new methods of hearing enhancement and treatment are becoming available. From hearing aids to cochlear implants, innovations are providing options for those with hearing loss. Understanding these technologies prepares healthcare workers to support patients in making informed choices about their auditory health.
Taking Action for Better Hearing Health
To wrap up, knowledge about how hearing works not only equips future medical professionals with essential tools but also prepares them to engage their communities effectively. As people become more aware of hearing health, they can seek help faster and reduce the stigma surrounding hearing impairments.
 Add
Add  Add Row
Add Row 



Write A Comment