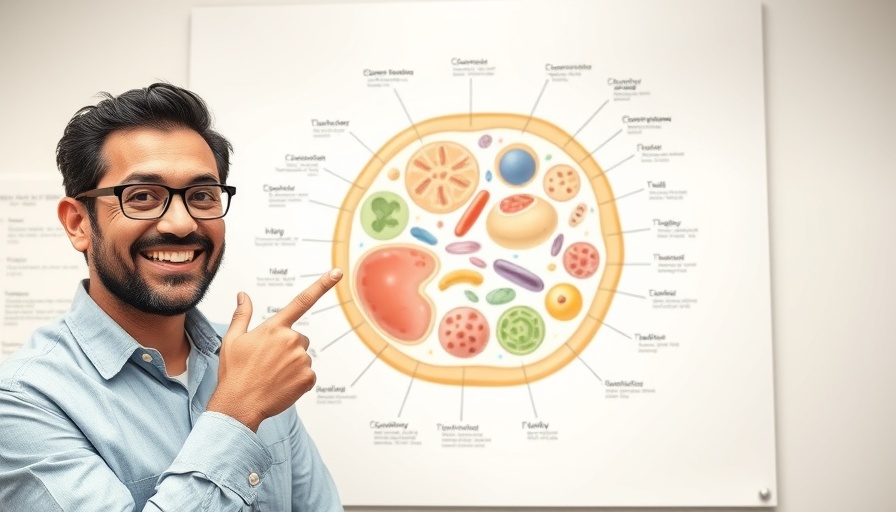

Understanding the Cell: A Complex System of Interconnected Functions
Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and understanding their inner workings is key for any medical professional or student. In the enlightening video titled The Cell and its Organelles, the intricate processes within the cell are broken down, making it easier to grasp how each organelle contributes to the overall functionality of this vital unit of life. This article explores those concepts while emphasizing their relevance for medical students and healthcare professionals in Uganda and East Africa.
In The Cell and its Organelles, the discussion dives into the fundamental processes of cell biology, exploring key insights that sparked deeper analysis on our end.
Key Organelles and Their Functions
At the heart of cellular processes are organelles, each specialized in specific functions. One of the primary components, the nucleus, serves as the control center. Here, DNA is housed, and through the process of transcription, it is converted into messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA then guides protein synthesis at the ribosomes. This step is metaphorically likened to following a Lego instruction manual—each biological instruction leads to the construction of essential proteins.
The Journey of Protein Synthesis
The process begins with the ribosomes translating mRNA into amino acid chains, which then fold into complex three-dimensional structures within the rough endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER). Here, proteins undergo modifications crucial for their function. These modifications include initial folding and quality control, ensuring only fully functional proteins proceed. Understanding this journey is vital for recognizing how proteins interact within the body and their potential dysfunction in disease states.
Importance of Mitochondria: The Powerhouse of the Cell
The mitochondria, often referred to as the 'powerhouse' of the cell, are responsible for generating ATP, the energy currency our cells require. This organelle utilizes nutrients and oxygen in a process known as cellular respiration, transforming food energy into a usable form. For medical students, grasping the role of mitochondria highlights the intricate connection between cellular metabolism and overall health, particularly in conditions marked by energy deficiencies.
Exploring the Role of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
In contrast to the Rough ER, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (Smooth ER) plays a significant role in synthesizing lipids and detoxifying harmful substances. Its interaction with proteins synthesized in the Rough ER highlights the interconnected nature of cellular functions. Understanding these processes can inform how metabolic diseases arise and guide treatment protocols.
Integrating Knowledge for Clinical Relevance
As future healthcare providers, comprehending the relationship between cellular function and disease is crucial. For instance, the storage functions of lysosomes, as well as their role in cellular cleanup and apoptosis, can be directly related to various medical conditions. This knowledge is particularly pertinent when addressing issues like cancer, where cellular mechanisms become dysfunctional.
Overall, the information presented in The Cell and its Organelles encourages a deeper exploration of cell biology, which is essential for effective medical practice. By understanding these fundamental principles, healthcare professionals can better appreciate the complexities of human health and disease.
As you delve deeper into the world of cellular biology and its clinical applications, consider utilizing additional resources for enhanced learning. Equip yourself with knowledge that not only informs your practice but also prepares you for future advancements in medicine.
 Add
Add  Add Row
Add Row 



Write A Comment